Cataract Surgery
Cataract extraction is one of the most frequently performed surgical procedures in the world with thousands of procedures performed daily all over the world.
The mains steps in Cataract surgery include:
1.Administering a local anaesthetic to the eye
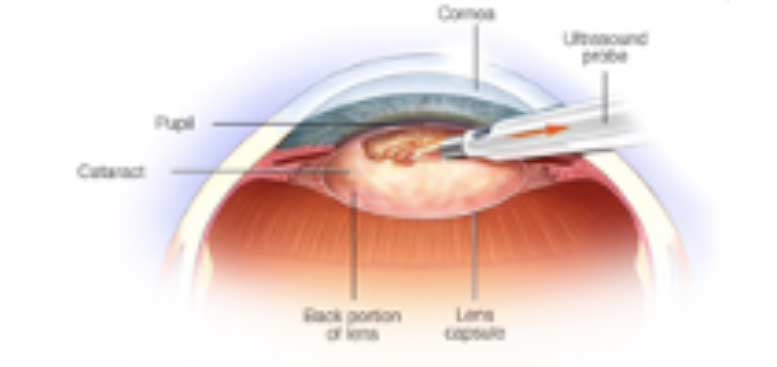
2.Making a tiny 2–3 mm incision in the outermost layer of the eye (the cornea)
3.Making an evenly round incision in the ‘bag’ (capsule) containing the affected lens
4.Breaking up the affected lens into smaller pieces with an ultrasound
5.Removing these pieces with a vacuum and flushing the lens capsule to clean it
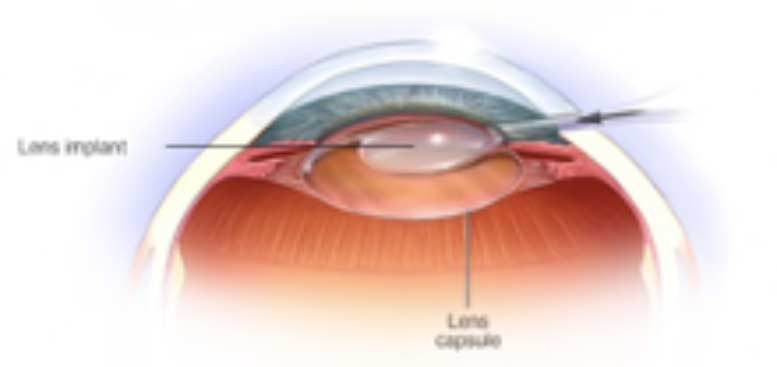
6.Inserting and accurately positioning a clear artificial replacement lens (known as an intraocular lens or IOL).
The new lens can’t be felt once placed inside the eye. When a lens is replaced, it is not possible to develop another cataract.
The operation itself takes less than 30 minutes and can be performed in a day surgery or in hospital.
Most patients will attend the next day for a quick check up and to receive advise about post-operative care following their cataract extraction.
Intra-ocular Lens Options (IOL options)
Artificial intraocular lenses (IOLs) are made of soft, flexible plastic and are used to replace your body’s natural lens. They can also be used to correct pre-existing refractive errors, such as short-sightedness, long-sightedness and/or astigmatism (blurry vision due to an abnormally shaped cornea or lens).
There are a number of replacement lens options available – the lens you choose will influence whether you still require glasses for certain activities following surgery.
1.Monofocal lenses allow clear vision at a single distance (i.e. near/reading or far). Following surgery, glasses will still be required for certain tasks.
2.Bifocal/multifocal lenses allow clear focus at two distances (i.e. both near/reading and far). These do not allow clear focus at intermediate distances, which is important for tasks such as computer work. Following surgery, glasses will most likely be required for certain tasks.
3.Trifocal lenses represent the latest in lens technology. These premium lenses offer clear vision at three distances – near/reading, intermediate and far. Glasses are often not required for standard day-to-day activities following surgery.
A premium lens refers to the more sophisticated lenses that offer greater flexibility and individual customisation. Trifocal lenses are a good example of a premium lens.
Patients should note that bifocal and trifocal lenses involve some visual compromise, meaning that they aren’t ideal for everybody.
If you are quick to notice visual imperfections or don’t mind wearing glasses, monofocal lenses are usually a better choice.
Toric lenses are used to correct astigmatism, where an abnormally shaped cornea or lens causes blurry or distorted vision.
Your specialist will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each lens type and help you select the right one for your needs. They will provide you with the full cost during your consultation, once you have chosen your preferred lens option.